Services / Dr. Ravi Bhanushali
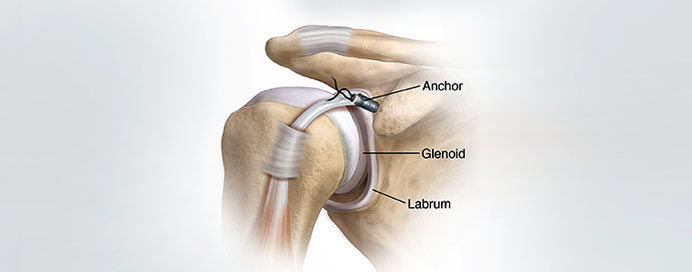
A Bankart repair is a surgical procedure performed to treat shoulder instability, often resulting from a tear or detachment of the labrum in the shoulder joint. The labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the shoulder socket, helping to stabilize the joint. When a specific type of labral tear called a Bankart lesion occurs, it can lead to recurrent dislocations of the shoulder. The Bankart repair is designed to address this issue and prevent further instability.
Here’s an overview of the Bankart repair procedure:
Bankart repair is often effective in restoring stability to the shoulder and reducing the risk of recurrent dislocations. The decision to undergo surgery is typically made after a thorough evaluation by an orthopedic surgeon, considering factors such as the extent of the injury, the patient’s age, and activity level.
