Services / Dr. Ravi Bhanushali
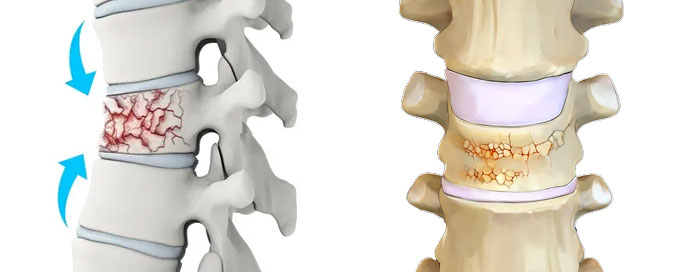
Osteoporosis is a medical condition characterized by weakening of the bones, making them more fragile and prone to fractures. It occurs when the body loses bone mass and density faster than it can be replaced, leading to a decrease in bone strength and an increased risk of fractures. Osteoporosis is often referred to as the “silent disease” because it progresses without symptoms until a fracture occurs.
Here’s an overview of osteoporosis and osteoporotic fractures:
Causes:
Symptoms:
Prognosis:
